Heat capacity is an extensive property the corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity dividing the heat capacity by the amount of.
Thermal heat capacity of air.
At normal atmospheric pressure of 1 013 bar the specific heat of.
Specific heat capacities of air.
Generally the most constant parameter is notably the volumetric heat capacity at least for solids which is notably around the value of 3 megajoule per cubic meter and kelvin.
The nominal values used for air at 300 k are c p 1 00 kj kg k c v 0 718 kj kg k and k 1 4.
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to a given mass of a material to produce a unit change in its temperature.
Specific heat c is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a mass unit of a substance by one degree.
Isochoric specific heat c v is used for air in a constant volume isovolumetric or isometric closed system.
Isobaric specific heat c p is used for air in a constant pressure δp 0 system.
Air has a heat capacity of about 700 joules per kg per k and a density of just 1 2 kg m 3 so its initial energy would be 700 x 1 x 1 2 x 293 246 120 joules a tiny fraction of the thermal energy stored in the water.
However they are all functions of temperature and with the extremely high temperature range experienced in internal combustion and gas turbine engines one can obtain significant errors.
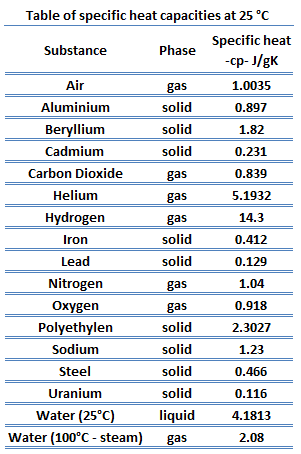
The following table of specific heat capacities gives the volumetric heat capacity as well as the specific heat capacity of some substances and engineering materials and when applicable the molar heat capacity.
The heat capacity called specific heat of air is 1 0035 joules per gram per degree centigrade j g c which is the same as kilojoules per kilogram per degree centigrade kj kg c.